Crystal structure studies. The approach to the analysis of the crystal structure of organic compounds based on the intermolecular interaction energies calculated by methods of quantum chemistry has been suggested. This approach creates the necessary prerequisites for development of a lot of directions for study:
- investigation of the influence on a type of crystal packing of the organic molecule fragments (substituents, type of hybridization of some carbon atoms, etc.);
- comparative analysis of the role of intermolecular interactions in the formation of crystal structure;
- disengagement of the levels of organization for molecular crystals: building unit (molecule or molecular complex), basic structural motif (column or layer) and 3D crystal structure; ranking of intermolecular interactions in crystals;
- comprehensive study of the relationship between crystal structure and mechanic or optic properties of molecular crystals; study of the polymorphism of molecular crystals based on the energy of intermolecular interactions.
The further development of this approach to the analysis of the molecular crystal structure led to the creation of a new method for predicting the properties of the crystal structure. Results about an “energetic” structure of the crystal under study can be used for further modeling. A model system containing one dimeric building unit as a mobile part and a fragment of its neighboring layer as a fixed part was extracted from the crystal structure. The mobile part was moved in relation to the fixed part and the interaction energies between mobile and fixed parts of the model system were calculated in each point. The energetic profile of such a displacement of the mobile part in relation to the fixed one can be used for the estimation of possible crystal deformation under external influence.
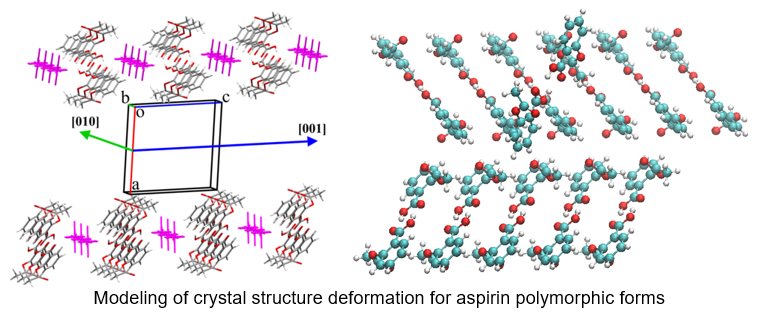
The energetic barrier for displacement of strongly bound fragments of crystal packing to each other as well as the form of the energetic profile near the starting point can be used for prediction of crystal behavior under pressure or high temperature. For example, the study of the displacement process in piracetam crystals has revealed a low energetic barrier and a local energy minimum near the starting point in the crystal structure before the phase transition. In contrast to piracetam crystals undergoing the phase transition, the mefenamic acid crystals proved to be stable to the pressure influence. The energetic profile of the displacement of strongly bound fragments has shown extremely high energy barrier and the absence of any local minimum at the starting point.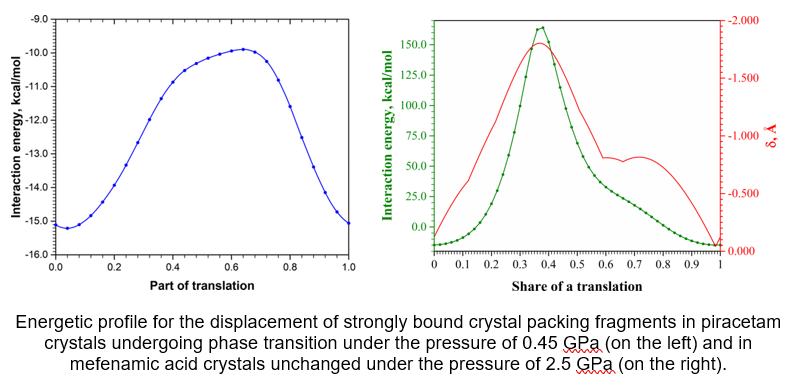
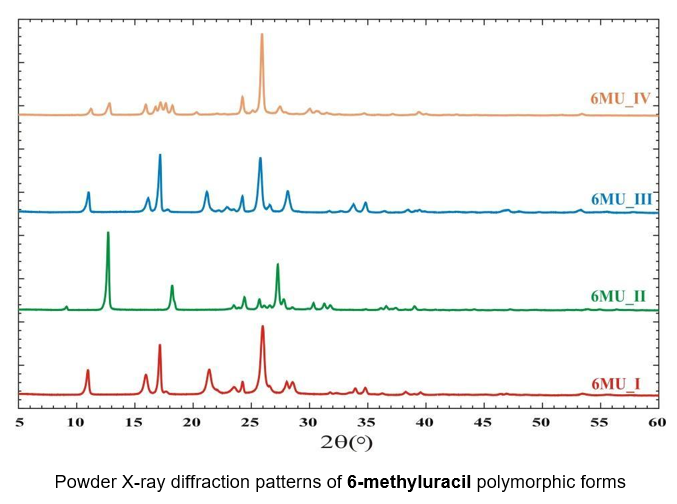
Complex application of powder and single crystal diffraction methods allows to perform studies for the pharmaceutical industry. As an example of such a study, the 6-methyluracil, which affects the regulation of lipid peroxidation and wound healing, has been analyzed by experimental method and the stability of its polymorphic forms has been estimated by quantum chemical methods. Two new polymorphic forms of 6-methyluracil have been found as a result of the sublimation process. The DSC analysis and quantum chemical analysis of crystal structures have shown that the polymorphic form used in the industry as well as two new forms which can be formed due to temperature increase are metastable. The modeling of the crystal deformation has shown that these metastable forms must be unchanged under pressure and can be tableted without any problems.
Various X-ray techniques to study the crystal structure of polycrystals, thin films, and superlattices. Determination of single crystals' crystalline perfection and orientation.
Titanium oxyfluoride (TiOF2)
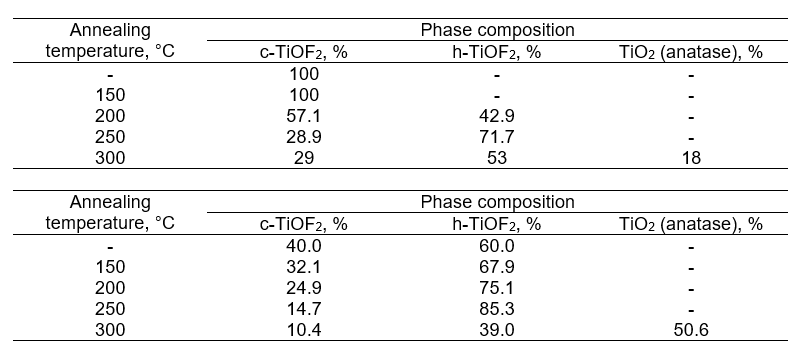
It has been discovered that the crystal structure of titanium oxyfluoride is affected by production conditions. It has been observed that it can exist in either cubic or hexagonal form. It has been shown that it is possible for TiOF2 to take on either a cubic or hexagonal structure, or a combination of the two. Additionally, irreversible polymorphic transformations have been identified when the material is heated within the temperature range of 150˚C to 300˚C
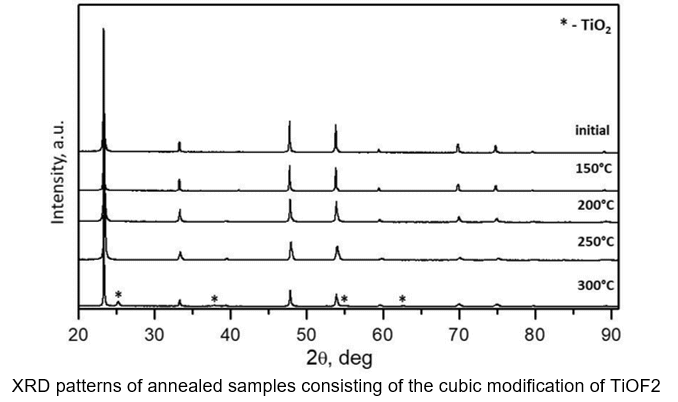
The Impact of Annealing Temperature on the Phase Composition of Samples Containing TiOF2.
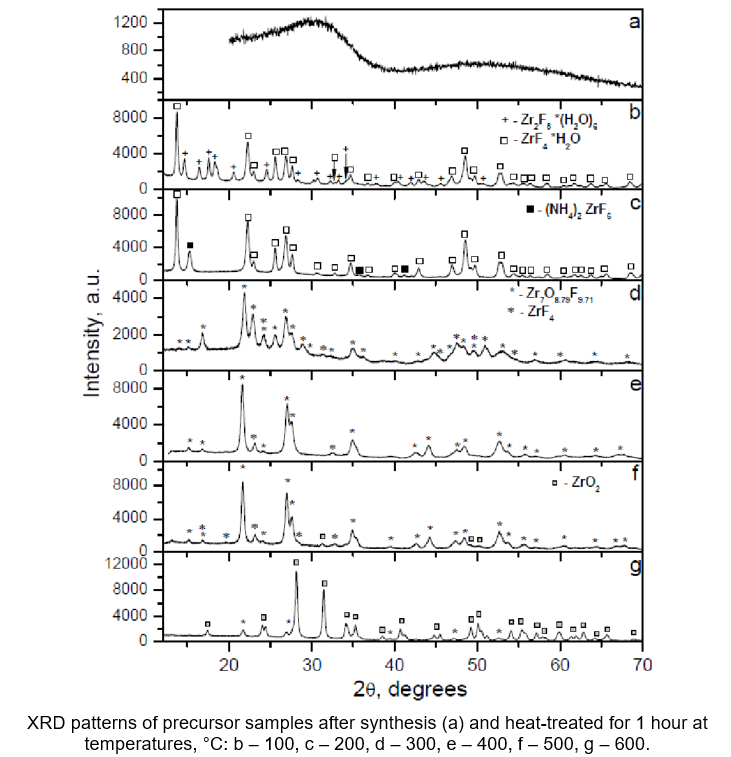
Zirconium dioxide powders for ceramic production
Upon phase analysis of the precursor samples, the processes that transpire during the heat treatment phase, particularly within the temperature range of 100°C to 600°C, resulting in the production of high-quality zirconium oxide powder were determined.